Across the globe, internet adoption has been steadily increasing over the years. In 2021, there are currently 4.66 billion active internet users worldwide. The Google Search Engine alone is servicing ~3.5 billion searches daily. This means that no matter what you do, there are people who are searching for your products and services online. To be more precise, ~93% of all online experiences are usually initiated by using search engines. SEO Basics is the term that is going to solve your tons of problems in the process of Learning SEO.
Toys, gaming consoles, smartphones, smartphone cases, and disposable face masks, are just a few examples of trending searches in 2021. But even though there are billions of web searches daily, 90.88% of the pages receive no organic search traffic from Google.
So how do you join the top 9% and start getting free and consistent traffic from Google?
This article’s main focus is to help you learn the basics of search engine optimization (SEO) so that you can understand how to attract free traffic from the world’s largest search engines. Even if you have no idea what SEO is, this article helps you learn SEO basics and you will have very clear and easy action items that you can implement on your website off the bat.
You will be covering the basic SEO strategies that you can use to ensure that your website is optimized for search. Later on in this guide, we will be going through the more advanced strategies.
Before you learn how Search Engine Optimization (SEO) works and how to do it, let’s first go over the definition of SEO, and then later we will get into the nitty-gritty of how it works.
What is SEO?

Any tech-savvy person can tell you that SEO is an abbreviation for Search Engine Optimization. But what does that mean? Are we optimizing search engines? On the contrary, SEO is all about making a lot of modifications which include but are not limited to creating great quality content, optimizing the content around specific keywords, and building backlinks to improve the user experience and performance of your website and web pages on search engines like Google so that you can get FREE ORGANIC traffic.
You are probably pretty new to SEO and you might be sitting there wondering how all these ties together. Well to get to grips with how search engines operate, it’s best to think of a search engine as a library. However, a search engine is not in the business of storing books. It instead stores and curates copies of websites and webpages from the internet in index entries. These indexes describe the location (URL) of the content. Therefore, when you search for a query on a search engine, it runs a deep search against all the pages in its database and tries to return what it considers to be the most relevant information based on your query. The reason why you should learn SEO is that you can use SEO concepts to convince search engines that your web pages are the result. Simply put, SEO is all about helping search engines understand that your content is relevant for a particular query so that they can present it to users. The best way to achieve this is by building websites that are geared toward making the user experience better.
Nowadays, SEO pretty much is targeted towards Google because they are by far the biggest player in this space. They dominate search on desktops, mobile, tablets, and game consoles.
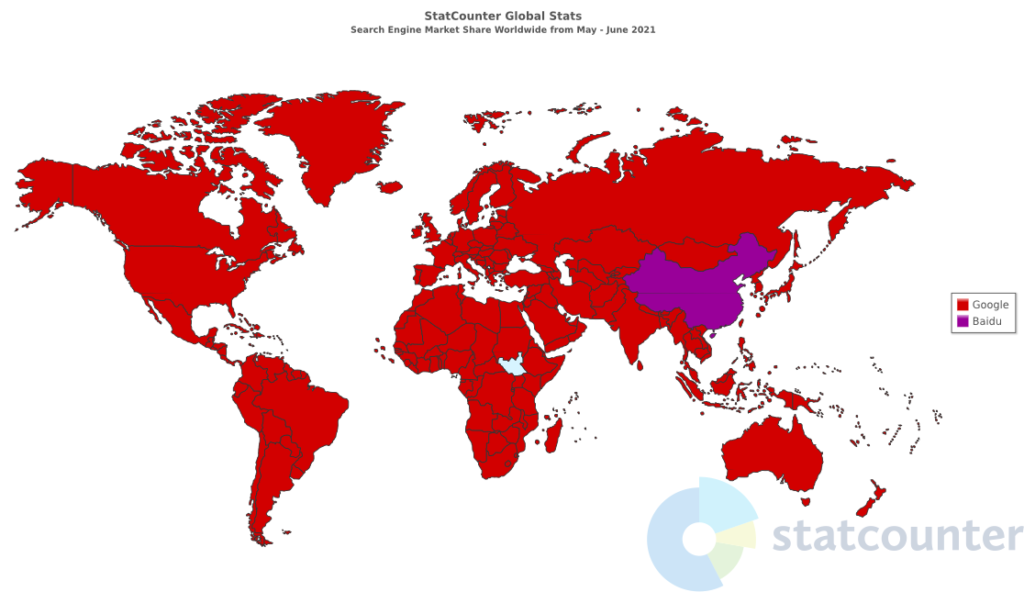
It’s therefore your goal as an SEO expert to make changes on your site so that the Google search engine can better understand it and help other users to discover your content. Google provides guidelines that if followed can make your site more search engine friendly. These recommendations include creating better content, changing how you structure URLs, as well as how to write good-quality titles and descriptions, and meta tags, just to name a few. They also provide free tools that you can leverage to boost your website’s organic rankings. They include:
1. Google PageSpeed Insights
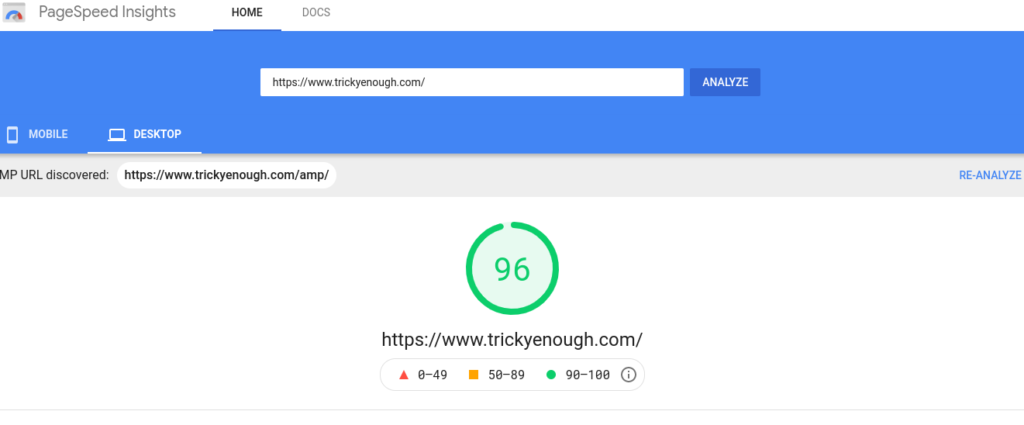
Google PageSpeed Insights (PSI) is an online tool that allows you to analyze the speed and usability of your website on both desktop and mobile and suggests areas of improvement.
2. Google Analytics
Google Analytics is a digital analytics service that is widely used by millions of businesses and SEO experts to provide insights during SEO campaigns. You can use Google Analytics to track and report on how users interact with your website in real time by monitoring metrics such as traffic sources, top referrals, bounce rate, session duration, pages per session, conversions, etc.
3. Google Search Console
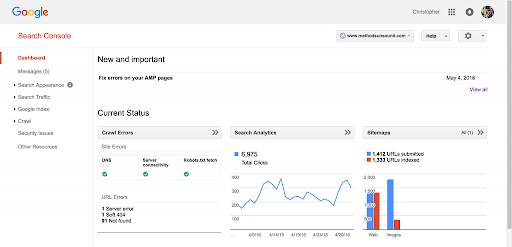
The Google Search Console is another powerful tool that you can use to monitor your website’s search traffic and improve your presence in the SERPs. It allows you to understand which queries drive traffic to your website as well as visualize your Website’s position in Google search. It also alerts you on issues when Google identifies them on your website.
4. Google Ads Keyword Planner
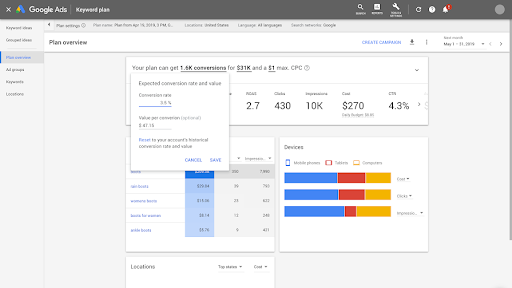
You can use the Keyword Planner to research and discover the keywords that fit into your business. The Keyword Planner provides actionable insights about the search volume that these keywords attract per month which can be leveraged to inform your keyword-targeting campaigns.
5. Google Mobile-Friendly Test
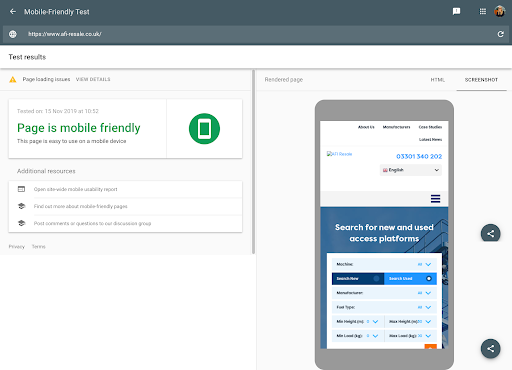
Many businesses still don’t appreciate the significance of a mobile-friendly site for SEO. The Mobile-Friendly Test tool allows you to see whether, you guessed it, your website is mobile-friendly seeing that a lot of online interactions happen on mobile devices. Mobile-friendliness is a major ranking factor that can boost your ranking in SERPs.
Why is SEO so important?

You might be wondering, why is it that you should focus on SEO when there are other marketing mediums that you can use to increase visibility. Well, are you aware that search engines are the starting point for 93% of all online experiences? Think of how many times you go on Google, Amazon, or YouTube and search. There are numerous search engines that proliferate the internet, and we use them all the time. Billions of people search online, for everything from hotel rooms to e-commerce products. This then means that there exist countless opportunities for businesses all over the world to reach out and be seen by new customers.
There are 3 major factors that attract marketers to SEO:
- Unlike paying for Ads, search traffic is completely free. In fact, organic search is one of the most profitable marketing channels.
- Organic traffic is generally consistent once you’re ranking high on Google. This traffic lasts even when you stop spending money on Ads whereas other media like email campaigns and social media campaigns often result in traffic spikes.
- You have the opportunity to reach massive audiences that you wouldn’t have access to otherwise.
This is why, in the United States alone, SEO is an $80 billion industry. Businesses are competing to appear on Google’s first page Google because that’s where all the action is, and SEO is the secret to achieving that. Good SEO practices don’t just increase your visibility on search engines, but they also improve the overall user experience, whether on your website or on SERPs. Think of SEO as your 24-hour salesman for your business so that no matter the time of day, or the country you’re in, you can get traffic and some of it will lead to sales.
Let’s suppose that you are the owner of a small computer store located in Ohio and that you want to expand your business by selling your products online. SEO will help search engines understand what you have to offer. Therefore, when a potential customer in Ohio submits a search using a keyword or phrase related to your business, such as best laptops under $300, there is a decent possibility that your store will show up in their results. This is because when a search engine returns results, the listings are a mix of paid ads that are normally placed at the top of the results page followed by organic results that have their place by convincing the search engine that they are relevant to the phrase that the user is searching for. Ranking higher in organic listings (non-paid section) is a result of applying SEO techniques effectively by, for example, creating better content, having a superior site with a good user experience, and using the best keywords.
When you optimize any given search word or term for a search engine on your site, it has a direct correlation with the amount of success you get from the campaign.
Benefits of Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
SEO Benefit #1 — Boosting traffic to your website
There are nearly 2 billion active websites online, and just having a website doesn’t cut it. Your position in search engines is everything. A solid SEO strategy makes it incredibly easier to drive qualified traffic to the content that you are publishing on your website. By optimizing the information that you are publishing toward your customer’s needs, you can position your website to rank higher in SERPs. This will in turn drive more traffic to your site compared to other sites in the same niche.
SEO Benefit #2 — Generating a positive ROI
You can supercharge your growth and ROI by leveraging SEO strategies to increase your visibility and acquire better leads that lead to increased conversations.
SEO Benefit #3 — Boosting your brand awareness
SEO is great for branding. Although predominantly used to drive more organic traffic, the same strategies can be used to establish brand visibility, authority, and recognition.
SEO Benefit #4 — Building authority, credibility, and trust
If it’s on Google, it must be true. By creating genuinely relevant content that contains keywords, and getting your audience to leave reviews and share the content, you can easily build credibility online and get more people coming back to your site for more information about that subject.
Search Engine Basics: How Google Search Works?
Google has invested heavily in its search engine to ensure that users can discover relevant and useful information on the open web from high-quality sites.
Before delivering search results to users, there’s a lot that occurs behind the scenes. There are three parts to how Google Search works:
1. Crawling
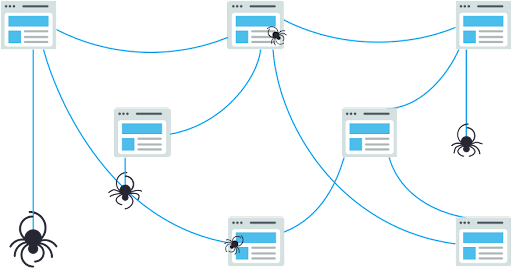
The first is crawling and this is how Google finds web pages that are new or recently updated. To discover new content, Google uses special automated search bot programs called Crawlers to scour through publicly available information from all over the web. The crawlers will often start crawling from a list of known pages from past crawls called Seeds, and they then follow the hyperlink URLs from those pages to discover new pages which are then submitted for inclusion in their indexes. This cycle repeats itself non-stop, and this enables search engines to crawl billions of web pages. Other pages are also discovered when webmasters submit sitemaps to Google for crawling.
2. Indexing
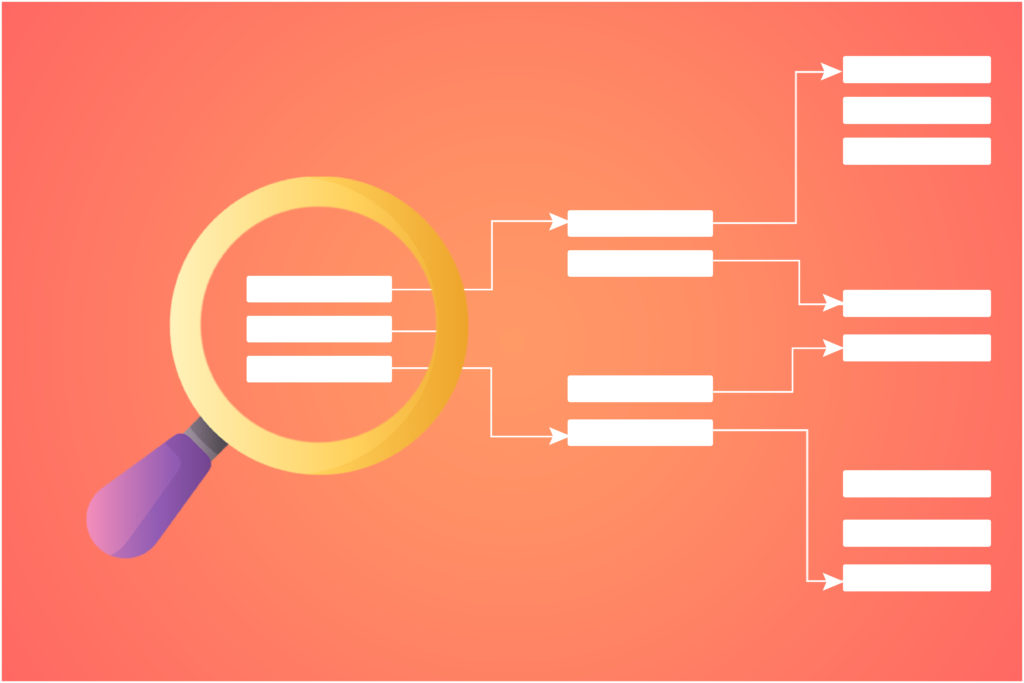
Indexing is the next step after crawling. It involves organizing and storing the pages in the search index (a large database that stores billions of web pages) and then analyzing all the content in the URLs such as text, images, videos, and other files so that the search engine can better understand what the web pages and sites are all about. The search index is where you get your results from when you submit a query in the Google Search box. Where your website appears in these results is affected by how popular your site is, the quality of your content, how you use page headings to convey the subject of the page — as well as other factors so that the search engine can present the best possible results based on the searcher’s device, geographic location, interests, etc.
3. Serving and Ranking

If Google were to return all the results that mentioned the words you type in a query, then you’d end up with very bad results. This brings us to the third part — Google’s Ranking Algorithm. The ranking algorithm tries to return the most relevant answer from its index based on many factors such as the words in your query, your age, past search history, geographical location, language, the reliability of the sources, etc. For example, when you search for “hotels” on your phone, you will most likely get local results because the algorithm is trying to show you nearby hotels that you’d like to visit. If you search for “news”, you are most likely to get the latest content.
There are hundreds of ranking signals that are working behind the scenes to provide the most relevant results. So instead of trying to game the algorithm and design your page for that, you are better poised working on creating authentic high-quality content that your target users want as well as following their guidelines and best practices recommendations.
How to Improve Serving and Ranking?
Factor 1 — Make Your Page Load Fast
A fast web experience has long been a well-known focus in web development. Google considers it to be an important user experience factor. This is because users generally care about page speed. They want to have access to answers as fast as possible. Every 1-second delay in page load translates to a 7% reduction in Conversions according to HubSpot. That is why Google added how fast pages load as a key metric in their ranking criteria. You can use the PageSpeed Insights tool to test whether your website loads fast.
Factor 2 — Make Your Website Mobile-friendly
The number of people using mobile devices is going up, so much so that Google has a mobile-first index. They introduced mobile-friendliness as a factor in ranking results since most people that use Google are already using mobile devices. To make the results more relevant, Google switched to a mobile-first approach where they only consider the mobile version of a website’s content when ranking pages. Therefore if you only have a desktop site, you should consider making it responsive so that it renders equally for mobile and desktop.
Factor 3 — Create High-Quality Content And Keep It Up To Date

Search engines value unique, engaging, relevant content and the rule of thumb here is that you should create a lot of it because it will help you rank for a lot of different keywords. So the question becomes how much content should you actually have and to what extent does it help your performance?
Well, websites are all about creating content and how much of it you require depends on what you’re doing. If you’re a News site, then you should cover as much as you can, but if your website is only about a specific product, then there is only so much you can say about that particular product and just stuffing content about the same product on your blog doesn’t say much.
For example, search engines know that if you have pages on Kayaking, then you may cover topics like; How to Kayak, Kayaking equipment, Best places to Kayak, Is Kayaking Risky, so the more details that you go into each page about the same topic, the higher you’re going to end up ranking in SERPs vs if you go really broad on a bunch of random topics, but you don’t go in-depth on all of them.
Factor 4 — Use Simple and Short URLs
Another factor is the URL length. The longer the URL length the lower your rankings are. Simple URLs as opposed to long and cryptic URLs that contain few recognizable words tend to be more user and search-engine-friendly. So you want to keep your URLs simple, short, and to the point with words that are readable to rank better in search results.
Factor 5 — Search Intent
The intent of the search query is a very strong indicator for search engines because their job is to find and show the most relevant information. Search intent represents the primary reason behind a user’s query. When it comes to search, the main purpose of the search engine is to help users to obtain the most relevant information based on their queries. But search engines are made of computer programs, they are unable to read and comprehend text in the same way that you and I can.
Nevertheless, Google as well as other search engines have poured a lot of research into creating sophisticated algorithms that understand the context and the relationship between words and concepts. However, it’s not exactly perfect and it’s your responsibility to make it easier for the search engines to understand the context of the subject.
You should publish content that is in line with the intent and questions of your target audience so that you can address their queries in the best way possible. It’s also important to know that depth doesn’t always lead to content length. For example, the question ‘How to take a screenshot on an iPhone 12’ doesn’t need to be and shouldn’t belong.
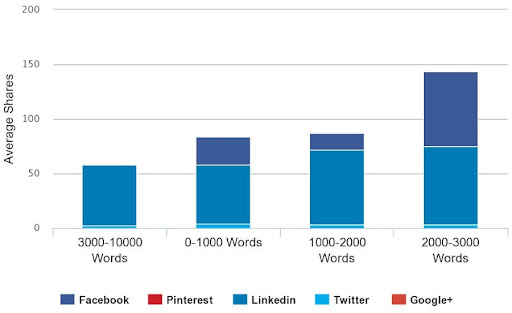
Generally speaking, the longer your content, the more engagement and social shares you’re going to end up getting. But that doesn’t mean releasing long articles that contain fluff. If you have fluff in your articles you won’t do well.
Factor 6 — Backlinks
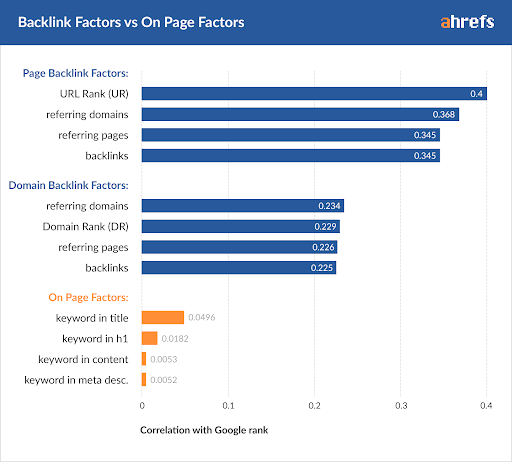
Backlinks are another major factor. Backlinks are links on a page from one website to another. If other prominent sites link to your page, Google’s algorithm will consider it to be good proof that the information on your site is authoritative and trustworthy. To understand the importance of backlinks, it’s probably best to consider them as votes.
When a page receives a backlink from another website, that website is essentially endorsing its content — at least that’s how Google sees it, and if you get a lot of reputable websites (preferably in the same niche) that are linking to your site, Google is going to take notice and trust your content.
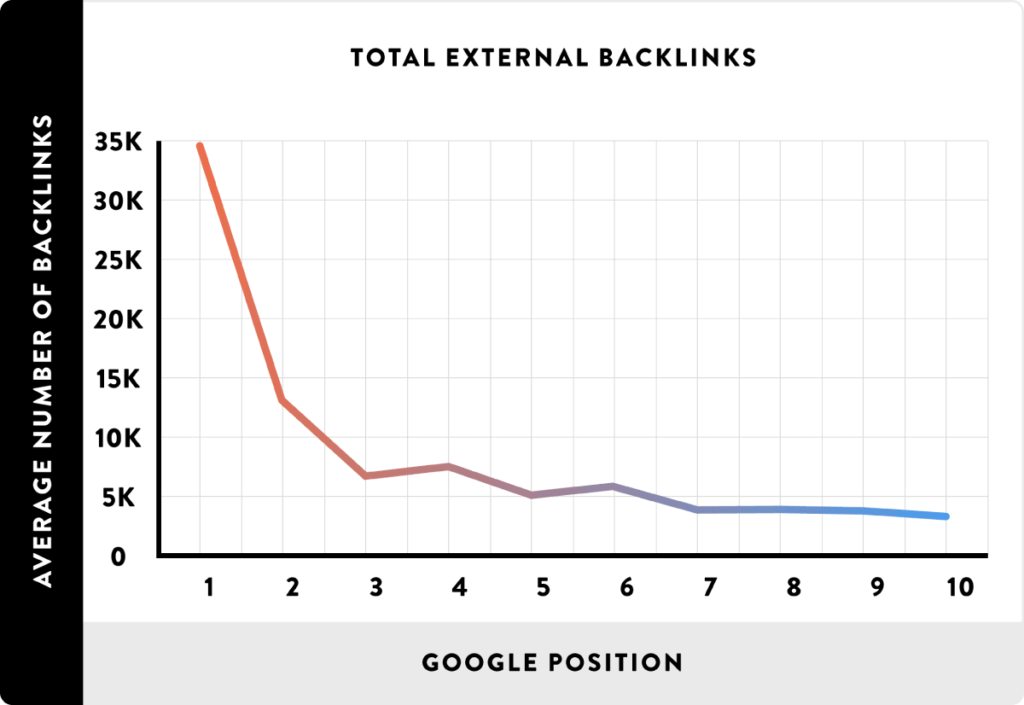
From this chart, it is evident that there is a direct correlation between the number of backlinks a page has and the organic traffic it receives from Google. So it’s super important to get other sites to link to you.
Check out this resource for a more in-depth explanation of link building for SEO and how to do it in 2023:
Factor 7 — Brand Power and Social Signals

Big brands are already successful and generally more reliable to offer the best information.
As a response to the declining quality of search results powered only by on-page signals ( which are easy to game ), Google came up with a classifier to sort the major brands such as the New York Times, The Wall Street Journal, Amazon, Wikipedia, etc from other lower-quality sites. These changes that favor link building have given businesses that work to create brands an advantage over smaller sites since their offline presence naturally leads to backlinks from news articles, social mentions, etc.
Factor 8 — Secure Your Site’s Connections With HTTPS Encryption

These days security is a major concern so you want to make sure that your site is using an SSL certificate so that you get HTTPS encryption. This is because when people visit your site and you don’t have SSL they’re more likely to get a warning. The Google search ranking algorithm uses this as a metric when determining where to rank your site.
The search algorithms will consider hundreds of other factors when serving results therefore this is not an exhaustive list. How these factors are weighted varies based on the nature of the queries.
Organic Listings vs. Paid Search ads
Organic and paid search are two of the prominent strategies that are applied by digital marketers. When you go on Google and use it to search for something, you will be presented with two types of search results:
- Paid search ads
- Organic listings
As the name suggests, paid search ads result from marketers spending money on pay-per-click (PPC) ad campaigns to rank higher in the search engine results pages (SERPs). On the other hand, organic search results appear as a result of content marketers applying SEO techniques to rank higher in SERPs listings.
Both strategies can help you boost traffic to your site. The major advantage that paid search has over organic search is that Google positions paid results at the very top of the SERPs with organic results placed just below that.
Summary
Content marketing is evolving rapidly, and as such, business owners need to stay abreast with the latest SEO strategies to keep up with the search engines that they value the most—and make sure their websites are optimized for them.
