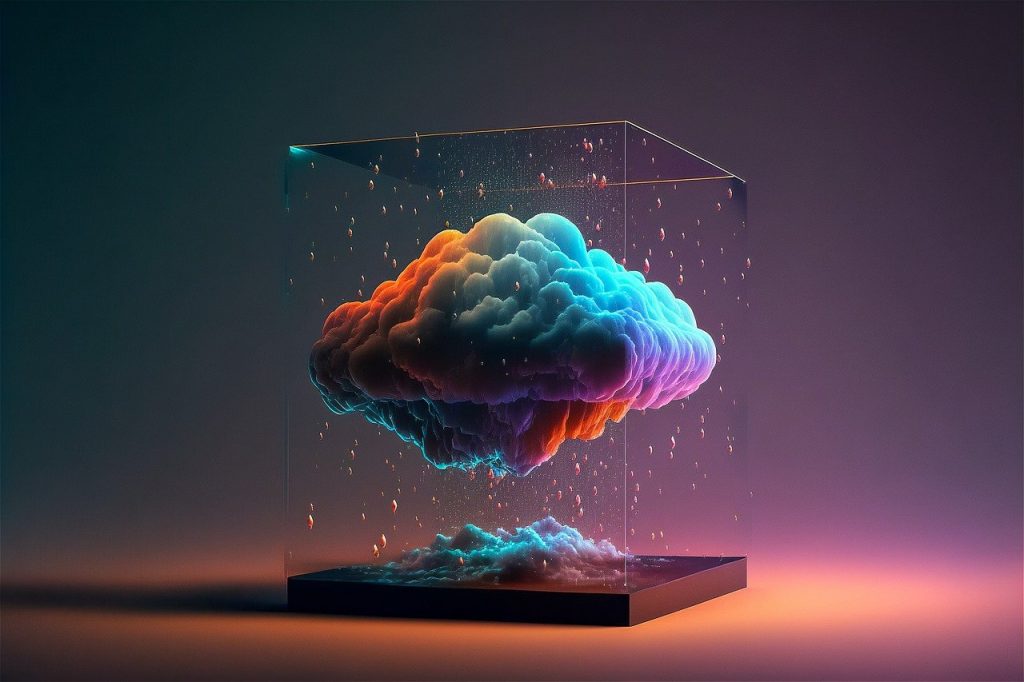
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way we work. It is believed that The global public cloud market will cross $146 billion in 2017, which is up from just $87 billion in 2015 and is growing at a 22% compound annual growth rate. It has proven to be a scalable, flexible, and cost-effective method of doing business.
While cloud computing has changed the face of IT and provided a one-stop solution for all business needs, it also poses some risks. What do you think when you hear the words Edward Snowden, Sony Corp., and Panama Leaks? All of these involved massive data breaches which adversely affected companies and governments. It’s clear that freedom and feasibility come at a price.
Suggested post:
Learn Cloud Computing in simple terms.
To combat these risks, your cloud service provider should seriously prioritize data security. Customers can have the best security and reliability in the market only if this technology is managed carefully.
How does data security in the cloud work?
Just like any computer program, cloud security also involves the same fundamental issues. Restricting access to authorized users, maintaining data integrity, and ensuring the availability of data. Safeguarding the data assets which reside externally on the campus is an added concern in cloud security. One of the best ways of transporting this data is by encrypting that data in transit.
To maintain data security in the cloud, the frequency and reliability of backups are very important. Cloud computing uses server virtualization, and if that virtualization isn’t secure, data from one segment of the server could leak into another area. Recovery of data, in the case of damage, is also a key responsibility of cloud service providers. So, cloud computing and data security go hand in hand.
“There are more opportunities for cybercriminals with the increased penetration of smartphones and other mobile devices, as well as the growth of the Internet of Things and wearable technology. These endpoints, together with the social engineering of credential information, means that there are more vulnerabilities through which organizations can be targeted.”
Security is a dire necessity for online users. One of the most popular myths about the cloud is that it is not secure enough. Users think that the data stored in the cloud can be accessed by anyone, anytime.
Suggested Post:
Types of Security systems that exist and you knew not.
However, the truth is that cloud computing is a secure way of doing work, especially for small businesses. There is no need to hire IT professionals or train them to perform certain tasks as cloud providers are already trained to provide the most modern security measures to their clients. Cloud providers also keep their infrastructure safe from hackers, and all of this comes at a much lower price than what you would pay for an in-house IT department.
Here are some other ways that your company can benefit from using cloud services:
Encryption
One of the best ways to secure data in the cloud, encryption is usually used for data that is in transition so that data is protected when it is traveling from one place to another. But encryption can also be applied to data that is at rest in the cloud, on a storage drive.
Cloud providers keep their storage drives secure, but some providers leave the password decryption key in the software, which can make it easier for hackers to obtain it. Global business services company Minter Ellison says the estimated cost of cybercrime will be US$6 trillion by 2021. That is why some cloud providers are more vigilant in keeping your data protected compared to others.
Keeping this in mind, you must know that every cloud service that hits the market is not right for you. Therefore, when you are choosing a cloud service, it’s best to run a comparison between the Giants and assess the better one based on your needs. Also, look at how the cloud provider implements infrastructure and how it can protect your company’s data efficiently.
Proactive governance
To ward off growing cyber threats, deploying secure cloud services is the first step. Proactive security governance includes secure coding, master management of policies, log maintenance, and data dictionary.
“The moment you have a non-standard infrastructure, non-standard protocols, and non-standard coding practices, cracks are visible. Also in the Cloud, the first thing that is enforced is discipline. No matter how hard we all are prepared, security incidents will happen because hackers have the element of surprise and they will perpetrate risk,” says Rutyunjay Mahapatra, Chief Information Officer (CIO), State Bank of India.
Identity and access management
Identity and access management are the keys to using cloud services in the best way possible. Businesses should centrally manage their own credentials and provide role-based access to authorized personnel only. This lets the user access systems even when they’re far away from the immediate organizational network. Strong security is combined with a user-friendly experience that lets users continue the work without disruption.
Since hackers are now choosing to deploy next-gen technologies to find a way inside your systems, a more mature policy is to recognize that inbound perimeter protection is not enough. Both cloud providers and clients can work together to secure access points at their ends.
Cloud security gateways
Gartner a well-known person in the field of security, defines cloud security gateways as on-premises or cloud-based security policy enforcement points placed between consumers and providers to interject enterprise security policies as cloud-based resources are accessed.
Cloud security gateways consolidate multiple types of security policy enforcement. Examples of security policies include authentication, single sign-on, authorization, security token mapping, encryption, tokenization, logging, alerting, API control, and so on.
Along with cloud providers tightening security around their systems, governments have also started passing regulations regarding cloud security; Canada, Germany, and Russia are drafting stricter data residency and sovereignty laws, which require data to remain in the country in order to protect their citizen’s personal information.
Failure to adequately protect your data can have huge consequences, including the potential for fines by one or more government or industry regulatory bodies. Such fines can be substantial and potentially crippling for a small or midsize business. For example, violations of GDPR data subject access rights can result in significant penalties for non-compliance, further emphasizing the importance of robust data protection measures. Additionally, the Payment Card Industry (PCI) can impose fines of up to $100,000 per month for violations of its compliance. Although these fines will be levied on the acquiring bank, they’re likely to impact the merchant as well.
Last words
To combat the risks, cloud service providers must have a fundamental understanding of cloud computing data security, and data sovereignty. These facts will help you build a foundation to ensure you are getting the best service from your cloud provider and that the security at your end is top-notch.
Suggested:
Public Cloud Computing: Basics for Beginners.
Like this:
Like Loading...












 7 Steps for Making Blogging as Full-Time Career
7 Steps for Making Blogging as Full-Time Career
This is an informative piece that definitely all organizations need to understand about cloud computing. With the increasing data breaches and GDPR enforcement, organizations, big or small, should implement.
Very well written Erica Silva. Cloud computing is gaining popularity as it is easier to manage (since virtualization saves space, etc.) with fewer footprints. I am a big supporter of cloud computing if there is need to manage too much of data across various users. There are many companies out there offering cloud storage and data security and most of them are quite good.
Hi Erica,
Very good article on security point on cloud which growing day by day.
Thanks for sharing this. Keep writing articles like this.
Cheers!
Hello Erica,
That was really a great piece of technical writing on what cloud computing is and how to secure data in the cloud environment. You helped better to understand what level of security is required in which level of the cloud computing.
Thanks a lot.